BPS Technology - Data Driven Models for Multi Currency Trade Brokerage and Loyalty Schemes
![]()
BPS Technology(ASX:BPS) helps businesses by attracting additional customers via their capability to deliver improved personalisation to the customer and investing in modern payments, trading, rewards and loyalty platforms developed econometric models optimised with data-driven insights to provide advanced analytics capability and business insight (www.bpstechnology.com).
QSpectral developed econometric models optimised with data-driven insights to provide advanced analytics capability and business insight.
This included:
- Development of a “Quantity of Money” theory for a dual currency exchange
- Machine Learning for extracting significant patterns in trading
- Time series analysis to provide forecasts
- Synthetic Control to control to establish causality and identify actions to improve future returns
- TIBCO Spotfire dynamic dashboards linked to on-demand calculations for consumption by various stakeholders.
QSpectral also developed a Price Discrimination model for a voucher system acquired by BPS Technology and extracted actionable insights from data based on this model. This modelling is expected to form the basis of a digital, personalised and auction based loyalty and voucher platform.
Acumen Data - Analytics for Complete Accounts Payable System(CAAPS)
![]() Requirement:
Requirement:
Acumen Data is an emerging leader in automated accounts payable solutions, providing customised Accounts Payable(AP) systems that meet individual business needs and improve processing efficiencies. As a component of this automation within the CAAPS system there was a requirement to autonomously detect duplicate as well as other irregular payments.
Solution:
- QSPectral used its advanced Data Science capabilities to firstly develop algorithms for mathematically detecting irregular transactions based on a number of criteria obtained from domain experts.
- These algorithms were validated by the payments processing expertise within Acumen data.
- A representative score was assigned based on the severity of the detected irregularity.
- We helped Acumen Data implement the method within corporate enterprise systems.
Future:
- Developing Machine Learning algorithms that learn the irregularities as the system is in operation
- Developing algorithm to learn typical user interactions to automate processing.
VenturePredict – Data Driven Decision Making for Investors and Entrepreneurs
Requirement:
 VenturePredict creates value for investors in startup companies (Angels, Venture Capitalists, Accelerators, and others) through a simple-to-use scoring tool – driven by data-science. They had a requirement for data science based R&D in:
VenturePredict creates value for investors in startup companies (Angels, Venture Capitalists, Accelerators, and others) through a simple-to-use scoring tool – driven by data-science. They had a requirement for data science based R&D in:
- Developing a methodology to increase investment hit-rate
- Reducing screening cycle-time and associated overheads
- Helping startups identify strengths and weaknesses
The methodology was to be incorporated into VP’s prediction and analysis platform.
Solution:
We proposed a data analytics based method to analyse potential investments and create a regime of data driven decision making to optimise investor portfolios.
- Firstly, a heuristic methodology based on business, economic and venture theory was formulated.
- These rules were calibrated based on empirical data.
- Machine Learning based multi-factor decision analysis was identified as an approach that can account for alternatives, contingencies and constraints to promote good decision-making under uncertainty.
On Going:
- Extraction of relevant data from startup eco systems
- Developing Machine Learning algorithms that learn the patterns of successful/un successful companies.
TRIP Medical Database: Liberating the Literature
 Article Association
Article Association
QSPectral used their data science expertise to investigate the connections between the articles based on the user access data contained within the Trip Database.
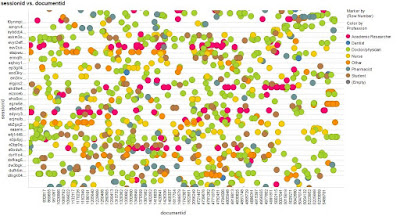
Figure 1 Snapshot of articles accessed across a session. The colours represent user professions (doctor, nurse, etc.)
In the above image the Y-axis represents individual search sessions and the X-axis is the documentID (each article in Trip has a unique document ID). So, we can see what professions are looking at which articles. We can actually see what articles individuals are looking at, but the above image shows it on a profession basis.
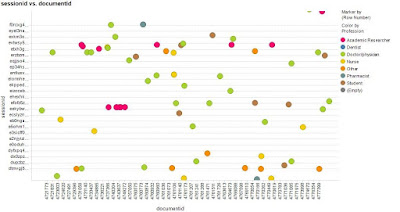
Figure 2 A more focused snapshot of the previous image
As a user do you want to see what other articles are similar to the one you are reading?
Do you want to know what others like you thought were similar?
To provide answers to these questions, QSPectral developed an algorithm based on association rules to explore the relationships between articles on a per session basis. We intended to identify links between articles based on different criteria of interest.
The strength of the links was measured by statistical measures such as confidence and support factors. These led to association rules, which were of the form if {article x is accessed then articles y and z} were also accessed were further enhanced by including additional user characteristics – information such as the profession (nurse, doctor..) as well as country of origin were used to moderate the previously established article relationships.
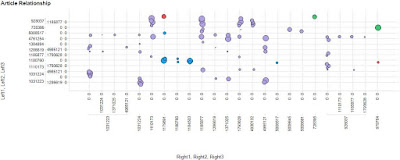
Figure 3 Snapshot of related article numbers – if the articles on the y axis are accessed it implies those on the x axis would also be of interest.
The data can be further augmented by adding clickstream data that includes the area of speciality (such as cardiology) for a user, where the for example, if you are a doctor from Spain only relationships between articles that doctors from Spain accessed could be isolated and uncovered. It was also possible to group the related articles in clusters based on this multi-dimensional relationship – defined by colour in the figure.
Figure 4 clusters of articles based on relationships
The purpose of this initial investigation was to set the stage for providing users with recommendations based on their initial article of interest and their particular user characteristic. A slightly different approach to PubMed’s ‘related articles’ feature.
As well as finding closely related articles QSPectral have helped us explore recommendations of new articles. So, if we know a user’s activity on Trip we can start to understand them and then – with QSPectral’s help – recommend new articles that should be of interest.
Article Recommendation
How will TRIP recommend articles for you?
Machine learning methods based on clustering and classification are being investigated for providing reliable recommendations.
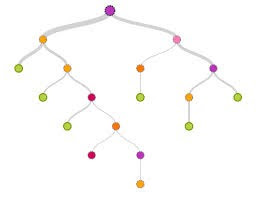
We believe that initial article clusters should be identified using an algorithm known as k-means clustering. Each user will then be classified as being interested in articles within a cluster based on attributes such as their first choice of article and user attributes (profession, country etc.) using a method where a tree-like graph or model of decisions and their possible consequences, including chance event outcomes, resource costs, and utility is created.
Figure 5 Example of a Decision Tree where the top node could represents you and the other nodes represent related articles based on branch criteria.
QSPectral determined that decision trees are the most appropriate concept for meeting the requirements. Decision tree methods can accommodate more data inputs over time. Various other transformations of inputs are possible and are robust to inclusion of irrelevant fields in the data, and produces transparent models for on-going analysis.
Further, we will use other methods that take a number of simple decision trees and combine them in some way to yield a final overall picture. We propose techniques for iteratively averaging multiple deep decision trees, trained on different parts of the collected data, with the goal of reducing the variance. Each iteration creates a simple decision tree on randomly selected subsets of input variables and input data. The final result where recommendations are provided will be formed through classifying a user through the aggregation of all such trees.
–
Centre for Biomedical Engineering, University of Adelaide
Requirement:
![]()
![]()
The customer required characterisation of the interactions between particles moving around in a box through modelling and simulation. The violation of the laws of classical Physics was acceptable in the tweaking of input parameters with the goal being to model output probability distributions reminiscent of those found in areas such as models of the stock market and small world networks.
Solution:
A software model was created in a manner such that key physical parameters could be altered during the input process. Simulation of the model showed that a slight non-physical increase in the coefficient of restitution lead to a tendency towards realising skewed Gaussian or fat-tailed distributions. This effect was further enhanced when particles were allowed to enter and leave the box according to a non-linear logistic equation. Rotational effects into the model and the Ricker formula to model birth-death processes were included in the model. Exciting new results showing that the final energy distribution was directly proportional to the degree of connectivity were obtained. The distributions for connectivity and energy were remarkably similar and consequently it would be possible to study network behaviour based on an energy parameter of the agents and their connections (collisions). This means that the analysis could be performed by considering well-known physical laws and perhaps quantified violations of them.
Centre for Internet Research, University of Adelaide
Requirement:
Evaluate adapting and implementing a high level (high order logic) petri-net based planner for logistical optimisation.
Solution:
Planning software in the international planning and scheduling community was evaluated with regard to the constraints and requirements of the exemplar logistical domains. Adaptations were defined and tested. Specific domain dependent controls for the planning software were also determined and incorporated into the tool.
Financial Modelling for a Hedge Fund
Requirement:
Develop and evaluate arbitrage strategies for a financial company.
Solution:
QSPectral developed statistical arbitrage techniques that worked across all market sectors in the ASX as well as implementing triangular arbitrage and covered interest arbitrage for Foereign Exchange trading.
Pit to Port Truck Haulage - sub contractor to major mining company
Requirement:
Optimise pit to port haulage operations
Solution:
QSPectral modelled the transport network and solved the optimisation problem using network flow models and queuing theory. The projected savings for the company based on the reduction of the number of trucks required was estimated to be in the millions of dollars.